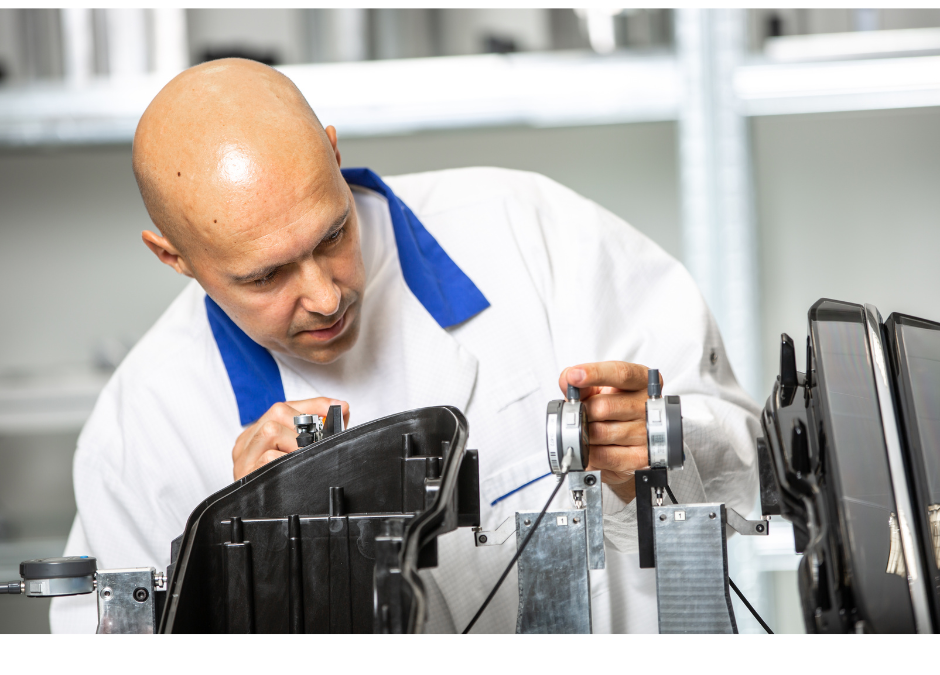
Metrology equipment enables manufacturers to precisely inspect product quality and identify deviations from design specifications. This equipment is vital for quality control across industries like automotive, aerospace, and medical devices that have stringent precision and consistency requirements. This article explores the most common types of industrial metrology equipment and their key applications.
Coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) play a pivotal role in precision inspection and quality control across manufacturing industries. By using accurate CMM measurements, manufacturers can identify and rectify deviations from nominal geometries early in the production process. This ensures consistency and prevents defects.
As an electronics, medical device, or optics manufacturer evaluating metrology adoption, understanding available equipment capabilities will be key for selecting the optimal solutions tailored to your workflows. This overview covers commonly used metrology tools across industrial sectors.
Coordinate Measuring Machines
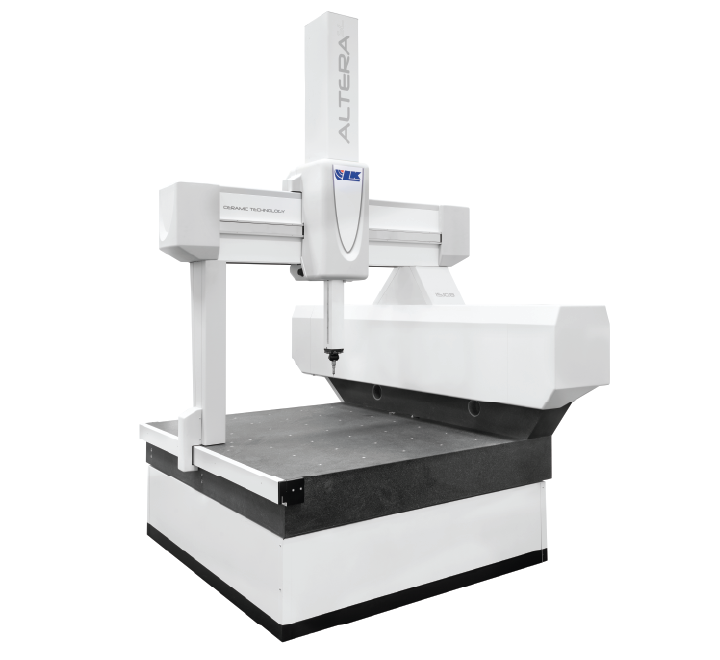
Coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) utilize an articulated arm with a probe to accurately map the dimensions, geometries and features of physical workpieces. There are three major CMM variants:
Bridge CMMs
Bridge CMMs contain a bridge assembly that moves along two fixed rails, allowing the attached probe to access a large measurement volume for inspecting large machined components or assemblies. The key advantage is the capability to handle large work zones spanning multiple feet. As an automotive or aerospace manufacturer, bridge CMMs suit inspection of oversized vehicle and aircraft sections.
Horizontal Arm CMMs
Horizontal arm CMMs can rotate around each of the articulated arm joints, enabling measurement of features from various angles. This dexterous configurability suits small to medium workpieces with intricate, hard-to-access geometries. As a medical device or electronics manufacturer, horizontal arm CMMs work well for precision small component measurement.
Gantry CMMs
Gantry CMMs utilize an overhead crossbeam that spans two side pillars containing guide rails. The probe moves in X, Y and Z axes along these rails, enabling accessibility over a cubic work zone. The stable gantry structure permits very high accuracy and repeatability. For electronics and semiconductor manufacturing needing reliable, high-precision inspection, gantry CMMs are an excellent choice.
The choice between CMM types involves tradeoffs between measurement volume needs, attainable accuracy, part sizes, multi-sensor options and budget. Identify capability targets for reliability, precision level and software functionality required before selecting systems tailored for your QA objectives.
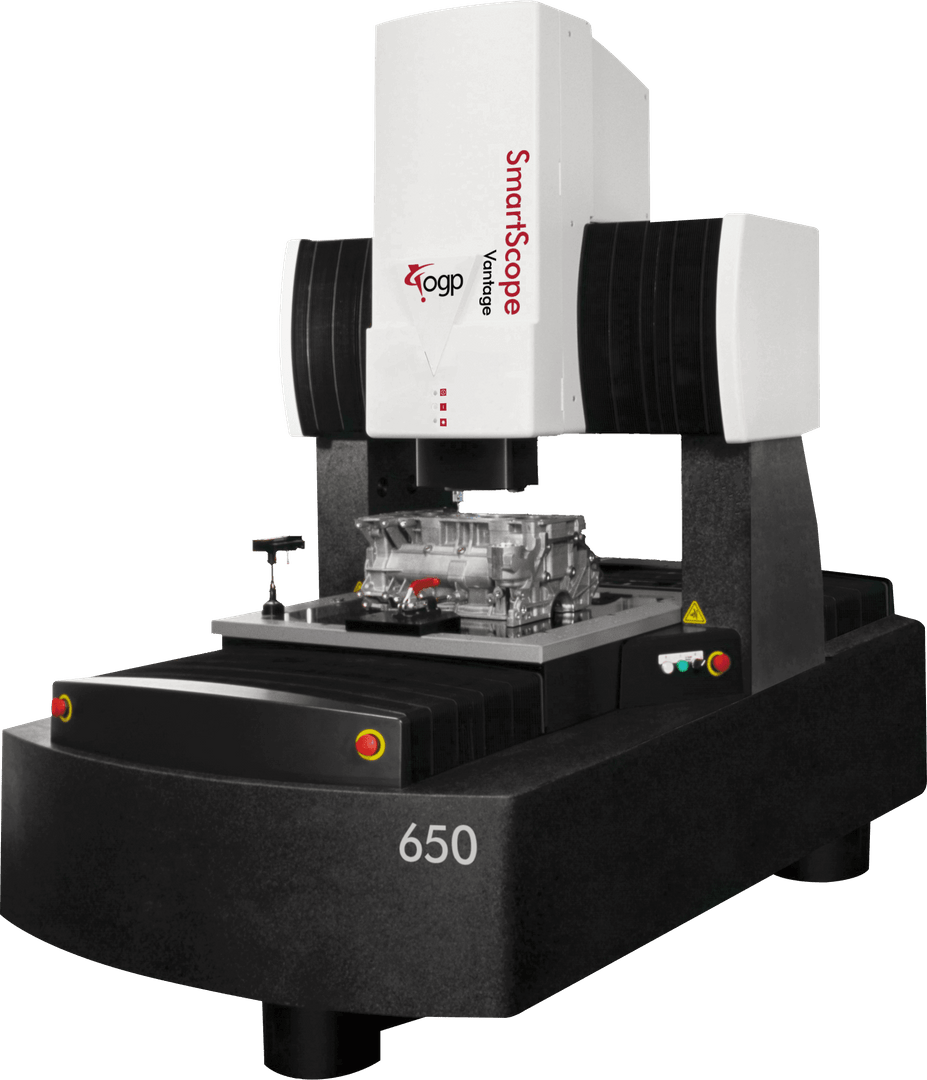
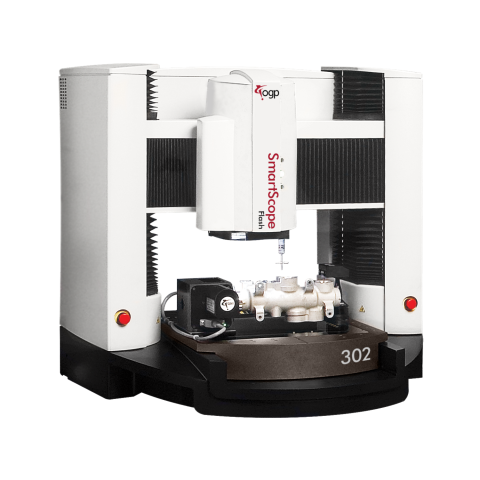
Vision Measurement Systems
Vision measurement systems use imaging and software instead of physical probes to inspect workpieces. Their capabilities allow fast, non-contact measurement of lengths, radii, angles, position and external workpiece features.
Optical comparators compare a magnified workpiece image against CAD templates for identifying surface anomalies and defects quickly. Easy to operate on production floors, optical comparators serve as viable solutions for electronics, medical, and electronics component scanning for aberrations.
Advanced automated vision systems with specialized lighting, high-resolution cameras, and featurized software enable collecting extensive visual datasets for sophisticated analysis, achieving exceptional accuracy rivaling physical probing methods. For thorough electronics and medical device inspection requiring non-contact precision at scale, these systems excel.
Laser Radar Metrology Systems
Laser radar systems, also referred to as LIDAR scanners, function by projecting laser beams onto work surfaces to determine distance and angle measurements with high accuracy. These noncontact scanners can access confined spaces while achieving precision capabilities.
Laser metrology scanners are available in various formats like line scanners containing rotating mirrors to sweep across areas for 3D mapping. Laser trackers dynamically follow target positions across large work zones. Laser radars mounted on robotic arms accurately reposition beams on-demand over changing measurement areas.
For industrial manufacturers seeking efficient means for alignment, verification, or calibration of large equipment and work cells, laser radar delivers flexible and transportable precision scanning solutions. Their noncontact nature also prevents damage to sensitive machine components while carrying out in-process diagnostic checks in semiconductors or electronics manufacturing lines.
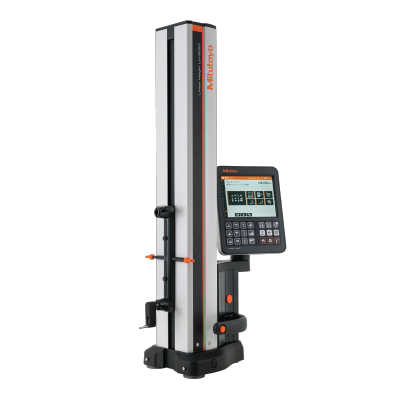
Form and Surface Metrology
Surface finish and form deviation instruments allow granular evaluation of intricate textures, flatness, roundness and other critical parameters per established industry norms vital for product performance.
Surface profilometers use a fine-tipped scanning stylus to map microscopic surface height variations, which software processes for detailed texture and flatness analysis. The nanometer resolution suits precision component finishing validation across production cycles.
Roundness measuring systems utilize rotary spindle-workpiece rotation and sensors to quantify circular form errors. This helps control production consistency for cylindrical automotive, aerospace and medical workpieces requiring stringent tolerances.
As quality needs grow more stringent and finishing processes more automated across sectors like automotive cylinders or electronics PCBs, purpose-built form and surface metrology systems enable manufacturers to tightly control standards compliance. Identify key form and surface metrics vital for your product performance upfront when adopting measurement solutions.
Find Your Metrology Equipment at Great Lakes
As an industrial manufacturer, choosing the right metrology tools tailored for application needs and workflows is key to maximizing quality control and efficiency. Great Lakes Metrology specialists can consult across inspection processes to recommend optimal measurement systems for upgrading quality assurance. By adopting high-accuracy, reliable metrology instruments purposed for manufacturing segments, rapid precision validation combined with actionable insights can be achieved to prevent defects and improve consistency.
To learn more about finding the ideal metrology solutions for your objectives, contact Great Lakes Metrology to connect with our experts.
FAQs
What are the benefits of multi-sensor metrology systems?
Multi-sensor metrology tools like CMMs equipped with touch probes, laser scanners and structured light projectors enable capturing multifaceted spatial data in a single setup. This allows comprehensive inspection while minimizing re-fixturing errors.
How does software analysis help leverage metrology data?
Modern metrology software offers extensive analytical capabilities to extract key trends and metrics from large measurement datasets. This provides valuable insights to optimize production for greater efficiency and consistency.
What industries utilize metrology technologies the most?
Precision component manufacturing industries like automotive, aerospace, medical, electronics and optics use metrology equipment extensively for design validation, pre-production qualification, in-process inspection and final quality assurance. Compliance to quality standards also necessitates high metrology usage.